Tuesday, May 08, 2020
Should business priorities dictate so much else?
Pressure from the “money men” is often blamed for increasing stress on managers and, through them, on the organization as a whole. Why should this be?Wall Street, like all stock markets, began as a way to raise money from people who wanted to take a share in the profits of the businesses that they invested in. Now it seems to drive everything else. At least when sharing in the profits is your goal, your interest is in a steady flow of good dividends. That’s a medium-term objective—maybe sometimes a long-term one too. So how did the modern craze for instant gratification arise?
Nowadays, most of the people on Wall Street are traders. They make their money by buying and selling shares, or gambling on share movements via so-called “financial derivatives.” Dividends are of little interest. Many businesses no longer pay any. Long-term success is also a minor concern, since few traders hold shares for the longer term. They want profits, and they want them now, so they can use them to trade some more.
The result is rampant short-termism. Buying and selling (trading) is essentially a short-term business. Besides, the traders have little or no interest in what they are trading, just as long as they can sell for more than they paid—hopefully in the shortest possible time—and move on. Hence the emphasis on quarterly figures as almost the sole criterion of success.
We also live in a time when it has become fashionable to believe that the ideas and practices of capitalist business apply to many other walks of life. Government departments, health care facilities, charitable organizations, even the arts all try to organize themselves based on the business world.
Capitalism may well be the best way that people have yet found for dealing with business and creating wealth, but it’s arguable whether its priorities should be the ones that determine so much of our lives. As a purely financial outlook, it has difficulty in dealing with “soft” human issues like compassion, altruism, and care. It cannot easily recognize value that can’t be counted or measured.
It would make more sense for us to accept that capitalism is the best we’ve done so far in one aspect of life, but keep it in its place. For the rest of our choices, other approaches need to be found. And even in the business world, I can see no reason why modern capitalist consumerism should be taken to be the last word. It may be as good as it gets at present, but that doesn’t mean we shouldn’t be using our creativity and brainpower to find even better, more civilized, ways of organizing wealth creation in the future.
What do you think?
Labels: civilized work, short-termism, thinking about management

Tuesday, May 01, 2020
Some plain truth about control freaks
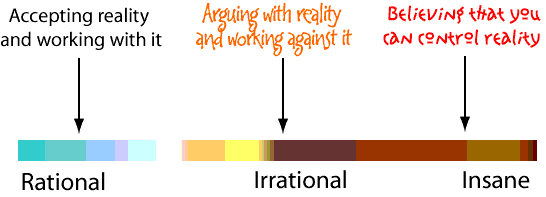
A posting by Dick Richards, entitled “Arguing with Reality,“ set me thinking.
So many macho managers spend their time either trying to control what is uncontrollable, or trying to force events back onto the track they wanted them to take, when it’s already too late. Much of the stress they suffer themselves—and cause in others—comes from doing this. Yet it’s not just tolerated. Such behavior is often seen as a mark of valuable determination and commitment.
Arguing with reality is illogical, pointless, and a total waste of energy and resources. That is the plain truth. Trying to control the uncontrollable is foolish, at best, and sometimes close to insanity. Control freaks are neither effective managers nor any kind of organizational asset. Mostly their irrational behavior is the cause of a great deal of upset, waste, and unhappiness.
It’s high time that people looked at conventional management attitudes and saw many of them for what they are: pointless, wasteful, and useless. Control freaks are sick. Arguing with reality is insane. Trying to control the future is impossible.
Let’s slow down, take a good, hard look at what people are doing in the name of management, and try to do better. Macho posturing is no course for any leader to take, whatever others do.
And don't miss reading Dick Richard's article.
Labels: management attitudes, thinking about management

Wednesday, April 18, 2020
A failing grade for the world’s business schools?
Are they a route towards a solution to today’s workplace issues; or a major part of the problem?
A little while ago, I posted an article about Professor Russell Ackoff’s “Management f-Laws.” Professor Ackoff, now 88 years old, has a mind as sharp as a razor and a subversive wit to match. These laws cleverly expose many of today’s conventional management ideas and assumptions as flaws in the process of running a business, not well-established steps to success as is usually believed. Here’s Ackoff’s take on business schools.Recently, Professor Ackoff was in London to promote his book. He was interviewed by Peter Day, the dean of British business correspondents, and the interviews are posted on the BBC’s web site. In this two-part article. I want to draw your attention to Professor Ackoff’s thinking about two issues critical to leadership and management: the role of business schools, and the impact of our modern culture of suppressing or denying many of our mistakes.
Here are some choice extracts from what Professor Ackoff had to say about business schools:
Business schools are way back. They’re behind even corporate practice. They are a major obstruction.Heady stuff, but not, I suspect, that far from the truth in many cases. Hamburger Management has infiltrated business schools in a big way, causing them to turn out mostly people polished in applying today’s orthodox style of macho, finance-obsessed, short-term management, not knowledgeable, thinking professionals equipped to make up their own minds and challenge sloppy thinking.
Information is more valuable than data, and knowledge more valuable than information, and understanding more valuable than knowledge. We devote all of our time and energy to information and a little bit to knowledge. None to understanding and still less to wisdom.
Peter Day summarizes Ackoff’s observations on business schools like this:
When he retired from the Wharton School in 1986, Professor Ackoff wickedly identified three contributions of a business school education:Let’s consider each of these points from a Slow Leadership perspective.
- It gives students a vocabulary that enables them to speak with authority on things they do not understand.
- It gives them a set of operating principles that enable them to withstand any amount of disconfirming evidence.
- It gives them a ticket to a job where they can learn something about management.
Does an MBA help people to speak with authority on things that they don’t understand? I suspect it does, at least in this sense. To understand something fully takes time and experience, plus a willingness to reflect deeply on what you have observed over many different situations. It used to be that expertise went with age; mostly because age allowed for enough time to have passed, not because older people are automatically wiser. Now bright, young MBAs are assumed to know more than managers twice their age.
Older people are often assumed to be out-of-date, technologically illiterate, incapable of grasping new ideas. Is this the truth?
Does time at a business school count for so much more than experience doing a management job? Older people are often assumed to be out-of-date, technologically illiterate, incapable of grasping new ideas. Is this the truth? No, just another one of those conventional cultural myths that bedevil all societies, like wearing top hats or growing luxuriant whiskers marked out Victorian times. There are older people who refuse to stay current, but I strongly suspect that they were just as reactionary when they were 20 as today, when they are 60 or older. There are many young people who care nothing about new ideas, preferring to rely on mindless slogans and whatever is the currently fashionable clap-trap. Getting an MBA gives you access to today’s fashionable buzzwords, that’s for sure. I’m not convinced it always offers much else. Maybe that’s why so many businesses suffer from jargon-monoxide poisoning and creeping consultantitis.In place of experience, we tend to rely on qualifications. Fine, if it’s also proof of some level of knowledge and hands-on training, as in the case of doctors. Not so good, if all it means is that you were able to absorb theoretical information and write term papers, as in the case of many MBAs.
What about the idea that business school student absorb a set of principles that are proof against all subsequent evidence that they are wrong?
. . . a whole generation of obsolescent executives, applying out-moded ideas together and never noticing they were doing it.
Also true. When I worked in management and executive posts, I came across hundreds of managers who had shown neither the inclination, nor the wit, to keep their knowledge up to date. Most relied entirely on a few basic principles they had learned maybe 25 years ago. They didn’t question them, because they had nothing to put in their place. Besides, questioning them would have taken time and thought, and they never slowed down enough to apply either. Since they were surrounded by others behaving in exactly similar ways, they appeared to fit in perfectly: a whole generation of obsolescent executives, applying out-moded ideas together and never noticing they were doing it.The last of Peter Day’s points does at least offer hope. The best way to learn about management and business is by doing it. You’ll get ample experience and have the chance to test your ideas in realistic situations. So far so good.
There’s one catch. You have to be willing both to make mistakes and reflect on them honestly afterwards. Pushing them aside, or hiding them from everyone (including yourself), renders this chance for learning null and void. And it’s not just mistakes arising from what you did that count. More problems are caused by mistakes based on not doing what you ought to have done.
But that’s the topic of part two of this article.
Labels: learning, thinking about management, thought leadership

Friday, April 06, 2020
Jam today . . . or caviar tomorrow?
Business leaders used to be compared to robber barons. Now some of them are more like greedy children or small-time gangsters.
Instant gratification is a hallmark of many of today’s organizations, headed by a slew of people following the shabby tenets of Hamburger Management. Sadly, there’s no sign that these organizations will grow out of their obsession; or that the financial institutions that fund them will encourage them to do so. This type of infantile behavior isn’t seen for what it is—a pathological prolonging of childish attitudes. In fact, people are encouraged to see it as perfectly normal. Why?David Maister raises some interesting questions (“The Long Term”) about people’s inability to get past their urge towards instant gratification to do what is best for their own long-term interest. He writes:
In much of my recent thinking (and writing) I have observed that our biggest barrier, as individuals and as organizations, is the difficulty in doing what is in our long-term best interest, not just what provides immediate gratification . . . it is part of the human condition that we can know what to do, why we should do it, and even how to do things for which we fervently desire the benefits. None of that actually predicts that we actually are going to do what we absolutely know is good for us.To say that this is equally, if not more, true of organizations is to state the obvious. The insane emphasis on quarterly earnings as almost the sole measure of business success is all about instant gratification. What may be in the longer-term interests of shareholders and the organization itself scarcely comes into the picture.
For organizations and individuals, it’s hard to resist the lure of “jam today” in favor of some future benefit that is, probably, far less certain. Taking the longer-term view used to be seen as a mark of maturity. Only children were expected to grab for immediate rewards. Adults saved money for the future, invested in pension plans, and considered short and long-term consequences before committing to some course of action.
What went wrong?
I suspect that much of today’s infantilism stems from a trend towards a consumer-based economy. Marketers and sales people don’t want customers to wait and think about their purchases. They don’t want them to set aside money in savings, when they could be spending it—right now—on buying products. From time to time, governments and financial gurus shake their heads over the problems caused by easy credit, but it’s really all their own doing. In the urge to sell more and more consumer products, credit is essential—and the easier the better. People quickly exhaust their current income (some still has to be spent on food and other necessities). Then they must either wait to save enough to make the next “big box” purchase, or borrow money to do so. Borrowing money not only makes the sale right away; it’s also a further opportunity to profit through the interest charged on the loan.
Somehow the consumer society manages to combine a puritanical obsession with working with a totally hedonistic devotion to getting whatever you want in as short a time as possible.
Yet capitalism itself is all about putting off gratification for the sake of greater long-term profit through investment. Instead of taking all their cash and having a truly memorable blow-out in some exotic location, entrepreneurs and capitalists are expected to invest their money and wait for bigger rewards some time in the future. Instant gratification is also the antithesis of America’s favorite attitude to life: the Puritan Work Ethic. If you truly accepted having it all and having it now as your goal, you would never go to work. Somehow the consumer society manages to combine a puritanical obsession with working with a totally hedonistic devotion to getting whatever you want in as short a time as possible.Whatever the rights and wrongs of a consumer society, it was, of course, inevitable that the attitudes produced should spill over into the rest of life.
Management practices are not immune from this process. Training and developing staff can be a long-term business—far too long-term for your average Hamburger Manager, who demands that everyone should “hit the ground running” or suffer the consequences. Developing sensible organizational strategies takes much more time than putting up a Powerpoint presentation of slogans and platitudes—or, better still, copying what some other, supposedly successful, organization is doing. Imitation may or may not be the sincerest form of flattery, but it’s a hell of a lot quicker than crafting ideas that exactly fit the needs of your own organization. Raising short-term profits by cutting costs provides almost instant returns, even if the longer-term impact may be dire. Raising them by improving products, service, or competitiveness takes a whole lot more time and effort—never mind that it’s the only way to create a sustainable future.
Only those that set aside infantile ideas of instant gratification and short-termism will make it through to influence and shape the future.
Maybe what we are seeing is Darwinian evolution at work. The mass of short-term, grab-and-go organizations and managers won’t have the staying power to survive. Only those that set aside infantile ideas of instant gratification and short-termism will make it through to influence and shape the future. For the rest, extinction will come far sooner than they expect—and much, much sooner that they would wish.Short-termism is an infectious disease that has been slowly choking the life and creativity out of our organizations. There's only one cure: to slow down, take a careful look at risks and rewards, and stop the slavish addiction to managing by numbers alone. Growing a business is like growing anything else. It takes time, and rushing it is more likely to produce a disaster than something that will go on growing. The attitudes of Hamburger Management have more in common with the methods of gangsters than entrepreneurs: get in quick, grab as much as you can, and get as far away as possible before trouble arrives. Is that what we want to see in boardrooms and executive suites?
Labels: corporate culture, Hamburger Management, short-termism, thinking about management

Monday, April 02, 2020
Unscientific management

Decision making by data collection isn’t management. It isn’t even sensible.
The current-day obsession with data and measurement is part of a supposedly “scientific” approach to management and decision making. Yet our equal obsession with speed and cutting corners ensures that choices are often made without taking enough time to weigh all the evidence, test it for validity, or even consider its true meaning. To parody Sir Winston Churchill: “Never in the history of human leadership has so much been measured by so many for so little resulting clarity.”We live in an age that prizes data and measurement to an almost obsessive degree. Computers have increased our ability to collect and process information by many orders of magnitude. Almost every special interest group, from political parties to social action groups and trade associations, trot out yet another slew of survey results whenever they wish to make a point or attract the attention of the media. No one seems to stop to ask what use we are making of all this data. Do we even know if it’s correct? Or what it means?
The media report all the often conflicting survey results with gleeful interest. Survey stories fill air-time and column inches. You can nearly always find some nugget in them to create a jaw-dropping headline. Never mind that today’s survey contradicts yesterday’s. The public attention span is assumed to be too short to care—or maybe even to notice.
Surveys and statistical studies have long been the stock-in-trade of academics. You publish your results, others test and criticize them, and—slowly—knowledge inches forward. If what you report fails to stand up to analysis and replication by your peers, it is rejected. You are an expert writing for experts. They demand solid evidence and unshakeable methodology. This process is the foundation of the scientific method.
Thanks to Powerpoint, presentations contain carefully chosen summaries—little more than headlines designed to produce an emotional reaction, not an analytical one.
In organizations, much of the data is collected and analyzed by amateurs. The methods used are often poorly understood. Once available, results are use more politically than scientifically: to justify individual points of view, support pet projects, or wave in the face of opponents. What supports a case is seized up. Often there is no one to question it, since any “inconvenient” findings are quietly hidden away. Thanks to Powerpoint, presentations contain carefully chosen summaries—little more than headlines designed to produce an emotional reaction, not an analytical one.It is the aura of scientific respectability that makes the day-to-day use of numerical data and survey results so attractive—and so dangerous. The results printed in the media, or reported in tens of thousands of Powerpoint presentations in corporations every day, are not delivered to be checked, questioned, or challenged. They are to be believed. All the scientific (or pseudo-scientific) trappings are used to foster an unquestioning acceptance of the supposed findings. The hearer or reader is subtly reminded that they are ill-informed amateurs being addressed by experts possessing all the data. This isn’t science. It’s marketing and PR “spin” wrapped in scientific garb. It’s a very aggressive wolf trying to pretend it’s a harmless, scientific sheep.
In today’s hyper-competitive climate, no one wants to admit that they understood barely one word in five . . .
In the workplace, more and more data is demanded, processed, and used to justify various points of view. Do those making decisions based on presentations of this data understand it? Do they have the knowledge, or the time, to question its validity—or even reflect on what else it might be pointing to, in place of whatever they have been told to believe? Is there any opportunity given for fact-checking or attempts to replicate the findings?The answer to all these questions is usually “no”. Haste is endemic. Executives are expected to make virtually instant decisions. Most of them are too overwhelmed with data, let alone all the other demands that they face, to do more than accept what their “experts” tell them. In today’s hyper-competitive climate, no one wants to admit that they understood barely one word in five; or that they have virtually no grasp of statistics and can be bamboozled by almost any set of plausible-seeming figures.
Worse, yet, many of the “experts” producing and presenting this data are consultants, and expensive ones at that. When you pay millions to get a report from a consulting firm, you aren’t usually disposed to question or reject the results. And the more that you’ve paid for the consultants’ findings, the less willing that you are even to consider that your money might have been wasted.
What does it take to make sure of a sensible level of fact-checking, critical analysis, and consideration of all this data, let alone the conclusions that you are told that it supports?
In management decision making, all data ought really to be presumed false or misleading until proven factual.
It takes time and the willingness to regard all proposals, however enthusiastically presented and wrapped in “scientific” analysis of data, with initial skepticism. In our judicial systems, people are presumed innocent until proven guilty (though try getting the media to respect that). In management decision making, all data ought really to be presumed false or misleading until proven factual; and all proposals supported by data, however superficially convincing, should be the subject of deep suspicion until proper independent evidence is produced.Time and skepticism: the very heart of Slow Leadership. Without them, managers and executives are almost helpless against manipulation by special interests and confusion by data overload. A glut of macho Hamburger Managers, all primed with endless ambition and eager to appear decisive, coupled with silly workloads and a corporate obsession with instant gratification, is a terrifying prospect. It’s like putting a group of manic two-year olds in charge of your trust fund.
Hardly a recipe for sound, truly scientific decision-making, is it?
Labels: Hamburger Management, leadership, priorities, strategic thinking, thinking about management, thought leadership

Monday, March 26, 2020
What a difference a word makes!
Why “improving motivation” is rarely, if ever, the answer.
Current ideas about motivation are a prime example of management theory and jargon twisted into the service of Hamburger Management. “Improving motivation” has become a group of impersonal techniques, to be applied to people in the way that you might apply a technique to herding cattle. What if we changed the words? What if we dropped all the talk about motivation used the word “encouragement” instead?Motivation is all the rage. It’s often seen as a universal requirement for everyone, whether they are expected to motivate themselves (as many self-help gurus proclaim), or to motivate those that they supervise (as legions of consultants and corporate trainers advocate). But what is motivation? Can it live up to the exaggerated claims now being made for its almost panacea effect?
At its simplest, motivation simply means “moving.” From there, it has come to mean moving towards some goal or end point. Self-motivation (as in: “Fred is able, but lacks self-motivation) is moving yourself in some definite direction. Elsewhere, it means little more than displaying energy and enthusiasm: a willingness to take positive action and utilize skills and abilities in the required direction. And in much official and business communication, the complex and abstract phrase “lacks motivation” is preferred—as more politically correct—to the simpler English “lazy” or “indolent.”
Motivation is also used in the sense of “making others motivated.” The verb “to motivate” is a staple in management jargon. Leaders are required to motivate their people—which means to cause them to do what the leader (and their organization) wants. How is this done? Typically, by application of the age-old process of “carrot and stick.” To get the donkey (or employee) to move where you want, you must either dangle a carrot in front of its nose (an incentive, bonus, or reward desirable enough to cause forward movement in that direction); or apply a stick to the other end of the poor beast’s anatomy (disciplinary action, punishment, withdrawal of privileges) to urge it forward in that way.
I am far from the first to wonder whether any leader can actually motivate another person in the way motivation is usually seen. Incentives (actually bribes) work for a time, but are subject to rapid inflation. Today’s incentive is tomorrow’s expectation. Punishments may produce movement, but they are hardly likely to produce enthusiasm. As has been found with the use of torture (or “strong interrogation methods,” if you prefer), people will say or do many things to stop the pain, but rarely mean any of them (or offer the truth, if something else will do just as well).
There is a fundamental problem with all the talk of motivation: it ignores or glosses over a search for the real causes of poor progress. Like so many other “techniques” that have become part of Hamburger Management, it’s a flashy, superficial, supposedly simple answer to an enormous range of largely unknown problems. What if we changed the word? What if leaders were expected not to motivate their people, but to encourage them?
Encouragement is a warm, natural, human activity; motivation is cool, detached, mechanistic.
Encouragement (literally, filling someone with courage) has little to do with either the stick or the carrot (save when it is used as a euphemism). To encourage someone, you must get to know them, find out their strengths, help them overcome their fears and the obstacles that hold them back, praise their achievements and support them through bad times. Encouragement is a warm, natural, human activity; motivation is cool, detached, mechanistic. Self-motivation could be replaced by self-encouragement: the process of helping yourself by building greater self-confidence and recognizing when your fears are the real obstacles to progress.When someone fails to make progress, or appears indolent and disinterested, there has to be a reason. It could be something in that person’s character. It could be that he or she is in the wrong job, or having personal problems, or feeling unwell, or missing some essential skill or experience, or is fearful of making a mistake, or lacks the confidence even to try. The list could go on and on.
Sadly, the typical Hamburger Manager has neither the patience nor the inclination to discover the truth. So a panacea—a catch-all solution—is quickly applied: motivation. First the carrot, then the stick. Then, if that fails (because willingness to move was never the problem), the person is labeled “unmotivated” and swiftly removed in some convenient way. It’s as if you got into your car, found that it would not go faster than 20 miles per hour, and either filled the tank with the highest octane fuel that you could find or kicked the bodywork hard as a solution to the problem. When both failed, you would next abandon the vehicle on the side of the highway and go buy another.
Wise managers see improving motivation for what it is: a simplistic group of quick-and-easy “answers” to difficult problems. Instead of joining in the frenzy, they step aside and do what great leaders, great teachers, and great mentors have done since humankind began. They take time with each person and encourage them to clarify, then solve, whatever it is that is holding them back from what they can and should become. They don’t do anything to the other person. They don’t apply a technique. They neither run ahead of the other, waving a carrot, nor press on them from behind, wielding a big stick. They walk beside them, seeing what they see and helping them to understand it in ways that shift a negative and frightening prospect into something positive and inviting.
Wise managers see improving motivation for what it is: a simplistic group of quick-and-easy “answers” to difficult problems.
Don’t try to motivate people. Encourage them. Don’t worry whether or not you feel motivated, Recognize what needs to be done and do it, trusting that you will find the stimulus that you need from the courage and confidence that will build within you as a result. Life is always movement. Trust it.Labels: civilized work, Hamburger Management, leadership, management attitudes, thinking about management

Tuesday, March 13, 2020
If feeling safe is good, does feeling good require feeling safe too?
How circular thinking corrupts management action
Much of management thinking is marred by sweeping generalizations, egregious platitudes, and faulty or non-existent logic. Few aspects are worse than the circular definition, where the converse of some supposedly true statement is also assumed to be true. Until we rid ourselves of such silliness, we will continue to chase mirages and put our trust in falsehoods.Management thinking of the conventional kind is full of circular definitions. They work like this, beginning with a statement that is mostly true, then reversing it and assuming that is also true. For example, getting results quickly is good (a vague, but mostly true generalization), which is then reversed to create the (mostly false) generalization that quick results are a measure of how good something is (getting results quickly is good, therefore good means getting results quickly).
Aside from being non-existent logic, such circular definitions do real harm. Take this pair: successful people are good to have around, therefore to be good to have around you must be successful. Since many of the causes of success (circumstances, luck) are outside people’s control, defining “good” as “successful” actually means basing your definition more on luck than expertise or judgment. Besides, some successful people are not at all good to have around, since their success breeds outsize egos and a prima donna attitude to everyone else.
What about this one: profit is what business is all about, therefore all business is about profit. The first part of the statement is questionable (it ignores the social and technical aspects of business), yet is probably broadly true. Yet the second part is neither true nor follows from the first. Much of business has little to do directly with making a profit, being concerned instead with product development, long-term growth, and the discovery and exploitation of new markets (which may not generate any profit for years).
My final example is this: what you can measure you can control, therefore you cannot control what you cannot measure. This has the distinction of being false in both parts. There are many things we can measure, but not control, such as rainfall, the growth rate of our children, and the buying habits of our customers. And as for not being able to control what we cannot measure, that may be true of leaders unable to control their tempers, their egos, and their greed, but it doesn’t apply to the rest of us.
Beware of circular definitions based on nothing more than platitudes and apparent symmetry. Hard-working people sometimes find success, but it doesn’t follow that success is always due to hard work. Sometimes, it is; quite often it isn’t. Even those who believe money brings happiness don’t usually claim that happiness brings money. So why should they assume that working long hours brings success?
I’ll leave you with this thought: if continually cutting costs boosts the bottom line, does improving the bottom line depend mostly on cutting costs? Many of today’s organizations act as if it does—which is probably why they are on a descending spiral of cutbacks and lay-offs, not an ascending one of greater creativity, expanding markets, and exciting new products. Compare Ford with Toyota and you’ll see at once what I mean.
Labels: corporate culture, management, management attitudes, slow leadership, thinking about management

Wednesday, March 07, 2020
Fishing for SCATE
A mythical creature still holds an irresistible lure for managers
A skate is a kind of bottom-dwelling, carnivorous fish, specifically belonging to the family Rajidae. A SCATE is something many managers seek—and periodically believe they have found: a Simple Complete Answer To Everything. Sadly, it is an illusion that creates havoc and leaves them struggling to recover from the effects of chasing after it.T here’s something irresistible about a Big Idea: one that promises to provide endlessly useful and yet simple answers to the most complex problems that people face. Most religions are based on one, and it provides the central core of faith that they demand. Politicians are suckers for Big Ideas, because they can be waved like banners to attract votes and are set down in simple, emotionally-powerful sound bites, instead of the complex trains of reasoning that politicians fear. Business leaders too love Big Ideas—not the sloganeering kind, but those of the type that I call a SCATE: a Simple Complete Answer To Everything.
A SCATE promises to provide all the answers in a deceptively simple way. In the 1980s, “business synergy” and “economies of scale” were the favored SCATEs. They fueled an orgy of mergers and take-overs, often creating companies that had to be expensively dismantled within only a few years, so badly-matched were the elements that had been used to construct them. In the 1990s, the Internet provided a SCATE of heroic proportions. Not only was it believed, with little or no evidence beyond wishful thinking, that the Internet was about the change the business world and global economics completely and for ever; any organization with “dot com” at the end was guaranteed to make money, however incomprehensible its business strategy.
 After the crash that followed, you might have expected greater caution, but the SCATE is a resourceful creature. Like the Questing Beast of Arthurian legend, it is made up of very odd parts (the Questing Beast had the head and neck of a serpent, the body of a leopard, the haunches of a lion, and the feet of a hart (deer). In T.H. White’s modern re-telling of the story of King Arthur (The Once and Future King), the Questing Beast lived only to be chased. When King Pellinore was persuaded to stop chasing after it, it pined and almost died.
After the crash that followed, you might have expected greater caution, but the SCATE is a resourceful creature. Like the Questing Beast of Arthurian legend, it is made up of very odd parts (the Questing Beast had the head and neck of a serpent, the body of a leopard, the haunches of a lion, and the feet of a hart (deer). In T.H. White’s modern re-telling of the story of King Arthur (The Once and Future King), the Questing Beast lived only to be chased. When King Pellinore was persuaded to stop chasing after it, it pined and almost died.In recent times, there have been several new versions of the SCATE, each one holding certain managers in thrall like love-sick teenagers: “business re-engineering” was one, then “downsizing,” and now “outsourcing”. Like the SCATEs of the past, they are flaunted as the obvious answer to just about every problem of business success, especially by consultants (who breed them specially, it seems, since they provide the easiest path to new consulting assignments).
Reality is complex, messy and uncertain. It takes time to understand, if it ever can be fully grasped, and still more time to deal with. There are no easy answers, though rationality goes a long way towards providing at least some useful options. Dealing with it is unspectacular and often tedious. Explaining what may work is also demanding and usually complex, requiring careful thought and listening to follow the logic.
Contrast this with the SCATE: simple to describe, often highly colored, offering endless promises with little or no effort required. Its adherents swiftly become disciples and treat any who are not true believers in their particular brand of revealed truth as enemies and heretics, to be drowned out with cheers or removed by force. Where reality must be described in lengthy and complex ways, the true SCATE is completely displayed through crude, often emotional appeals to “get on board” and “join the party” before the opportunity is lost.
Skates, the fish, devour what they can catch. SCATEs do the same, gobbling up managers and organizations as their food, swelling on the rich diet—until they explode, to cover everyone around in the mess left by their sudden extinction.
Don’t fall for them. Take your time and stick with reality. Remember, they exist only to be chased by those whose belief in their personal heroic status exceeds the capacity of their intellect. Better to be laughed at as an unbeliever than become a sudden ex-hero, lost, bemused . . . and covered with SCATE-sh*t.
Labels: management, management attitudes, thinking about management

Friday, March 02, 2020
The Perversions of Workplace Power
Today’s top executives have too much power and business is suffering as a result.
Feeling powerless, even over your daily schedule, is a major component of workplace stress. The inequalities of power in today’s organizations are too extreme. It’s time to restore a better balance.Hierarchies are all about power. Those in the workplace are no different. The people at the top exercise most power; those at the bottom have least—or none at all. I think that this is a simple fact of life. Some idealists may hope for a power-free workplace, but I don’t see that happening. Someone has to accept responsibility for making decisions and issuing instructions for others to carry out, or there is likely to be something close to anarchy.
What causes problems is not so much the unequal distribution of power as the degree of that inequality.
In dictatorships, all the power is held by an individual—like Hitler or Stalin— and everyone else must obey. In oligarchies—like the old Soviet Union after Stalin, or China today—power is concentrated in the hands of a favored elite. In democracies, power is far more widely distributed. An elected few hold some of it, but only subject to legal and political checks. Some is given to middle-ranking officials. And even those at the bottom of the social ladder have a little power, even if they can only express it at voting time.
Organizations are, generally speaking, not democratic. But that shouldn’t mean that the only alternatives are dictatorships or oligarchies run for the exclusive benefit of an elite.
Organizations are, generally speaking, not democratic. But that shouldn’t mean that the only alternatives are dictatorships or oligarchies run for the exclusive benefit of an elite. There is a wide spectrum available: from the kind of quasi-democracy of some small, high-tech organizations to the rigid oligarchies of most old-established corporations—or the quasi-dictatorships run by high-profile, egotistical CEOs in recent years.Those in power quickly come to resent any checks on their freedom to use it however they like. They try to remove checks on their freedom, and extend their power wherever they can. It’s said that all power corrupts. Maybe that’s true in one sense: it’s frustrating and irksome to have to submit your ideas and wishes to others for approval, especially if you fear they will be rejected or watered down. Top executives have usually spent years fighting for the power that they now exercise. They don’t like to give it up, even a little.
The more macho the organization, the more power matters. Organizations afflicted with Hamburger Management become obsessed by power struggles and ambition.
All the politics that go on in organizations are simply people jockeying for power and influence. It’s often easier to build greater informal power than to try to get the “rules” changed for your benefit. Influence and patronage, for example, are both potent sources of power, though neither appear on the organization chart. In nearly all organizations—especially large and complex ones—there is a constant process of shifting power structures. The more macho the organization, the more power matters. Organizations afflicted with Hamburger Management become obsessed by power struggles and ambition.The reality is that there is only so much power available. To get more, you have to take it from others. In the 1990s and early 2000s, CEOs worked to take power for themselves and away from boards of directors and shareholders. Of late, shareholders have been trying to take it back. “Rising stars” try to sneak power away from established leaders. Divisions and departments “steal” power from the centre whenever they can. Central functions typically write policies and procedures that deny power to subsidiaries and operating divisions. And everyone in the upper reaches of a hierarchy takes power from the easiest source: those lower down.
When people feel that they have no power even over their own daily work schedules, the results are instantly stressful.
Powerlessness—real or imagined—is one of the major causes of frustration, stress, and burnout. When people feel that they have no power even over their own daily work schedules, the results are instantly stressful. In the past, only slaves and servants had no power in this way. To be without power is to be reduced to a paid slave. What we see today is even highly-educated professionals being treated as serfs, to be allocated crippling working hours without the resources or the freedom to decide how to live their own lives.Disparities of power in the workplace are like wage disparities: everyone accepts that they will happen, but expects them to be held within reasonable limits.
We know that the CEO will earn far more than the lowest-paid worker. We accept that as reasonable. But when it is 400 or 500 times more, that looks very like an abuse. It’s the same with power. No one expects the workplace to be an idealized democracy. But when it becomes a dictatorship or an oligarchy based on a tiny elite, we smell the corrupting effects of an obsession with power.In a civilized society, all power must be kept under constant scrutiny, and any abuses detected and dealt with before they can turn into abuses. What we have today are corporations with too much power held in the hands of too few people. It’s producing stressful, toxic, and uncivilized working conditions for too many people.
It’s time to slow down, take a hard look at what is happening, and get back to a better balance.
Labels: burnout, civilized work, corporate culture, leadership, thinking about management

Thursday, February 22, 2020
Russell Ackoff: a wise and subversive thinker
How flawed, out-of-date, and misplaced teachings are crippling management
Professor Russell Ackoff has recently published a new book about the f-Laws, uncomfortable truths about the (mistaken) way most organizations are run, and how this approach is embedded in decades of repeated management mistakes and conventional business teaching. If you don't already know about Professor Ackoff, this article will introduce you to a grand old man of management non-conformity.
Here's a fascinating short piece from the BBC in London about Russell Ackoff and his f-Laws: the view that business is riddled with “flaws . . . from decades of repeated management mistakes and conventional business teaching.”
According to Professor Ackoff:
f-Laws are truths about organizations that we might wish to deny or ignore—simple and more reliable guides to managers’ everyday behavior than the complex truths proposed by scientists, economists and philosophers.Here are a few examples:
- The lower the rank of managers, the more they know about fewer things. The higher the rank of managers, the less they know about many things.
- Executives make mountains out of molehills; subordinates make molehills out of mountains.
- The relationship between executives and subordinates is complementary: neither knows why the other does what they do, nor cares about it. This leaves a large black hole between them into which most important issues and communications fall, lost and, like Clementine, gone forever.
In the workplace it’s also true that managers will measure anything that can be quantified in order to be able to set targets.Then there is this piece of wisdom from Sally Bibb, Professor Ackoff’s collaborator, that speaks directly to Slow Leadership and the current craze for over-ambition and Hamburger Management:
Managers don’t know what they want because they never think about it. One executive told his psychotherapist he was depressed because he felt he wasn’t successful. To the therapist he looked successful: good job, great salary, lovely family and beautiful home. She asked how he would know when he was successful. He couldn’t answer. He just kept on striving without knowing what he was striving for.Ackoff's books on the f-Laws are published in Great Britain, and you can get a free “taster” from the publishers. His latest book is Management f-Laws: How organizations really work
I’ve said in many posts that I believe traditional organizational ideas are out-of-date and badly flawed. We still owe far too much to methods dreamed up in the days of Henry Ford and the Model-T. Despite great books like Hard Facts, Dangerous Half-Truths And Total Nonsense: Profiting From Evidence-Based Management
Labels: leadership, thinking about management, thought leadership

Monday, February 19, 2020
Lies, Damned Lies, and Executive Platitudes
Why pretending to value people and acting otherwise is a corporate crime.
That handy platitude about our people being our greatest asset is trotted out in everything from press releases to annual reports to executive speeches. But does it mean anything? Is there ever any real intention to act on it? And if there is not, as so often appears, what are the implications for the businesses and organizations involved?Recently, one of the regular readers of this blog, Dan, mentioned in a comment that the business platitude about our people being our greatest asset didn’t often appear to translate into action. Corporations, and the executives who run them, may claim that “our people are our greatest asset,” but their actions certainly suggest some very different assumptions. Staff are habitually accounted for as a cost, to be limited and minimized wherever possible, along with all other costs. Aside from the obvious ethical implications of such casual dishonesty, what are the true implications for an organization that fails to treat people as an asset at all?
A good place to start is to explore what actions might we expect to see, if this phrase about people being assets (let alone the organization’s greatest asset) was acted on in good faith. Any business’s assets are carefully protected and nurtured&mdashit;’s greatest asset most of all. And that asset would obviously be the central focus of most business strategy. Not only would it be used as carefully and effectively as possible to build and develop the business, it also surely be enhanced and added to whenever circumstances allowed. If someone says that their home, or their 401(K) pension plan, is their greatest asset, you would expect to see them invest time, money, and effort in adding to its value whenever they could.
On this basis, the action that prove something is believed to be a critical asset include:
- Protecting and nurturing it.
- Making its use and development central to any strategy.
- Using it as well and as carefully as possible.
- Making it the central point around which other activities revolve.
- Working to increase its value whenever circumstances allow.
- People are treated as expendable and often subjected to rough and stressful treatment.
- They are rarely seen as central to any kind of business strategy.
- Far from using existing people to generate fresh ideas or come up with new projects, this is increasingly outsourced to consultants -- as if it is automatically assumed that internal resources are inadequate for handling anything other than routine.
- People are expected to fit themselves around financial and technical demands, not the other way around.
- Expenditure on increasing the value of employees (training, development, benefits) is seen as the first and most obvious target for cost reductions.
This type of casual reliance on platitudes that no one intends to take seriously represents a serious ethical lapse: an automatic and institutionalized level of dishonesty.
Politicians regularly try to deceive the electorate with “spin” and lies, and more and more business leaders seem to be using similar tactics. In both cases, the result is widespread distrust, anger, and resentment. Taken too far, such actions undermine the basic respect for authority on which all countries and organizations depend for stability.If business leaders fasten on the use of meaningless platitudes and “spin” as a way to sugar-coat their true intentions, they will wreck such trust as they still enjoy and create instead an atmosphere of continual suspicion. People are not compelled to work for a particular employer. They can refuse to join, leave, or (worst of all) stay to collect a paycheck, but give as little of themselves as possible in return. Destroying trust is both foolish and economically wasteful.
What would an organization look like if its people really were treated as its greatest asset?
Maybe it would be something like this:- Expenditure on people would be classed as a natural and laudable investment, not a cost. It would be among the last things to be cut in bad times.
- Staffing cuts and lay-offs would become so rare that their use would signal the very worst kind of crisis. Instead, an organization’s people would be seen as its most obvious source of ways to survive bad times, and the most value asset available to top executives in fighting off competition.
- Concert for the welfare and development of staff would automatically be number one on every manager’s list of priorities.
- As many staff as practicable would be involved in proposing more effective business practices and helping to develop strategy.
- There would be an automatic zero-tolerance policy for anything that undermined the value of the organization’s principal asset—its people—such as bullying, discrimination, dishonesty, cruelty, imposition of stress and overwork, or simply behaving like a total jerk. Bob Sutton has traced research suggesting that the presence of even a single asshole in a business has grave consequences on overall productivity.
- Each person would be seen as a source of unique value, so it would become mandatory to discover what they do best -- then help them do it.
- Executives would be expected to be leaders and mentors, working for the benefit of all, not autocrats and egotists focused mostly on their own aggrandizement and profit.
To my mind, that is close to being a corporate “crime.” It is certainly a gross dereliction of the duty of any executive to the owners or shareholders. Suppose some executive neglected maintenance and allowed expensive machinery to be ruined. Wouldn’t you expect them to be disciplined, or even fired? So what should happen if a boss treats people in ways that ruin their effectiveness through increased stress, lowered morale, limited creativity, or increased turnover?
Actions, it is said, speak louder than words. In the Christian Bible, it is written that you can know people’s true nature by their “fruits,” meaning the visible results of what they do. If many of today’s organizations were trees, their fruits would range from bitterly unpalatable to downright poisonous. It that any way for a civilized society to organize how it deals with work?
Labels: corporate culture, management attitudes, thinking about management, trust


This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 2.5 License.


