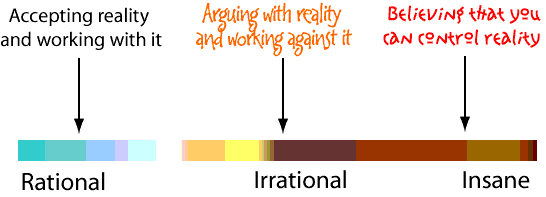
Listing the sins of macho management
Despite its popularity, macho management has many severe drawbacks.
If macho management is not a sensible way to operate, it must be possible to show why. Organizations won’t be convinced by saying it’s unpleasant, so long as they believe that it works in their interests. Here’s why it doesn’t.Macho management has become the norm because organizations have convinced themselves that it works to drive up profits better than the alternatives. They’re also convinced that the down-sides are minor compared to the benefits.
I believe that they are mistaken; but the proponents of macho, financially-biased management are so many—and so convinced of the correctness of their position—that it needs to be the opponents of conventional management who must make their case to overturn what has become the norm. That’s what this article tries to do.
Here are what I see as the most obvious drawbacks of macho management. There are probably more, but I have tried to consider my list from the point of view of managers, not ethicists.
- Pushing too hard. If too little effort is demonstrably bad for results, too much is probably worse. It leads haste and over-extended organizations; to harassment of customers and suppliers, careless mistakes, snap judgments based on inadequate data; to over-eager grasping of ill-understood opportunities and the taking of poorly calculated risks; to the forced suppression of contrary views, to lowered creativity, and to the alienation and loss of talented employees.
- Arrogance and egotism. Macho kinds of behavior come easiest to egotists. Research has shown that egotistical leaders are more likely to take both high-risk, even rash decisions and decisions based purely on self-interest.
- Blinkered viewpoints. In the rush and fury of macho culture, a constant is the tendency to see the world in black and white. Decisions are straight up or down. People, ideas, opportunities are good or bad. This departs so far from reality as to be dangerous.
- All-or-nothing bets. Macho managers aren’t patient enough for slow, incremental wins. They want massive, public success and will often take risks on a similar scale. All-or-nothing easily turns out to be the latter.
- Riding roughshod over others. Lots of macho managers have very short fuses—many are even proud of the fact. Their response to anything short of total agreement is to throw a tantrum. Intimidation is a way of life. All this produces is resentment and a desire to get even.
- Domineering attitudes. Command-and-control is the hallmark of every macho culture. Those at the top have to be in charge of everything. Lower manages are subservient upwards and tyrannical to everyone else. This is a great breeding ground for lawsuits, labor disputes, excessive turnover, poor morale, sabotage, and low quality work.
- Love of a good fight. The macho manager only shines during conflict. If there isn’t any, he or she is very likely to generate some. Conflict also wastes money, lowers productivity, promotes discord, and destroys creativity. Go figure.
- Fear-based decisions. Macho cultures are saturated with fear at every level. Fear of those with more power, fear of being stabbed in the back, fear of losing out, fear of failure and disgrace. People compete all the time—not so much to win as to avoid losing. The results include lying, cheating, trying to harm competitors, concealing errors, manipulating figures, and putting personal survival above everything else.
- Rampant office politics. In macho cultures, politics are everywhere. Where you stand in the political pecking-order is almost all that counts. Employees, customers, business ethics, rules, laws, and just about anything else become tools in various political fights between opposing barons.
- Inability to cooperate or share. Macho managers only share with their toadies, and then as little as possible. No real cooperation is possible. You can’t assist a potential rival—and no one who isn’t a rival is worth notice. Besides, all those barons have to maintain their status and influence against real or assumed rivals. In a macho culture, there is usually more strife internally than with external competitors.
- Constant turf wars. Not only are macho cultures extremely territorial, everyone constantly tries to steal territory from everyone else. Like bull seals competing for beach space and females, macho managers spend most of their time posturing, roaring, bickering, and trying to grab bits of territory. How this helps the organization is beyond me.
Given so many and such obvious drawbacks, it seems odd that macho management has so many followers. I think the answers are both simple and depressing:
- Once you have macho managers in place, everyone with a different outlook leaves or is forced out. The macho guys despise them. Macho management is the ultimate self-perpetuating system.
- In macho cultures, money is viewed as almost the sole measurement of results. That's why you typically find macho people in charge and hordes of accountants keeping the score. It’s hard to imagine a more soul-destroying environment—or one more likely to ignore everything that does not come with a price or a score attached.
- Changing a macho culture almost never happens peacefully from within. The status quo is strong precisely because it suits those in charge. It’s their status quo. It made them the people they are and guarantees their survival. That’s why they will try to squash anything that threatens it. And, being aggressive and action-oriented, macho managers are some of the world’s best enforcers.
Labels: executives, Hamburger Management, management attitudes, thinking about management